general information
A starter is an electric motor operating on permanent magnets, having an electromagnetic two-motor traction relay and a planetary gearbox.
Their cases are made of steel, six magnets are fixed to the case, and the case itself and the covers are tightened with several bolts. The starter armature shaft is put into rotation mode by two bearings, one of which, a ball bearing, is installed near the manifold, the second, a plain bearing, is installed next to the drive. Thanks to the gearbox, torque is transmitted to the starter drive shaft. The drive shaft is equipped with an overrunning clutch with a drive gear moving along the splines of the shaft. It is the clutch that ensures the transmission of torque from the starter to the motor, separating these elements after the engine starts. This condition ensures proper protection of the starter from possible damage that it may receive due to its high rotation speed.
The relay is designed to engage the drive gear with the teeth of the crankshaft flywheel mechanism, as well as to activate the starter power supply. Thus, by turning the key in the lock, the driver begins the process of supplying electric current to the starter from the battery. The starter is set in motion and turns the crankshaft, starting the engine and igniting the combustible mixture.
After starting the engine, the crankshaft speed begins to increase, however, the clutch protects the starter from damage. After the driver returns the key in the lock to the “ignition” position, the relay winding will de-energize and its armature will return to its original position, while the relay contacts will open and the drive gear will disengage from the flywheel teeth. At the same time, the power contacts supplying electric current to the starter motor windings will open.
In addition, the starter is one of the most powerful energy consumers on a car; when starting the engine, the electric current it consumes reaches 400 A or more. For this reason, all electrical connections between the starter and the battery must have reliable contact.
The elements that Grants are equipped with are similar to the starters used by VAZ on its other cars of previous generations. When the engine is in normal condition, two or three turns will be enough to start. Deviations from the norm will be indicated by any of the existing signs of unstable functioning. Possible malfunctions of the drive and starter relay will be revealed by inspection carried out after disassembling the part.
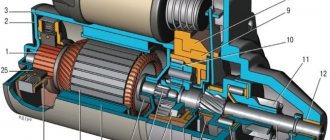
Main components of the Lada Granta starter
The figure below shows the constituent elements and their names in the starter of the Lada Granta car
Fig. 2. Parts of the Lada Granta starter: 1 - screw securing the traction relay; 2 — front cover; 3 - support ring; 4 — restrictive ring; 5 — lever support; 6 — freewheel; 7 — relay anchor; 8 — lock washer; 9 — return spring; 10 — spacer washer; 11 - traction relay; 12 — drive shaft support; 13 — drive shaft; 14 — planetary gear (satellite); 15 — planetary gear cover; 16 — back cover; 17 — brush holder fastening screw; 18 — coupling bolt; 19 — connecting bus with insulated brushes; 20 — brush holder with “negative” brushes; 21 — pressure spring; 22 — anchor; 23 — drive lever; 24 - body
Starter operating rules
According to AvtoVAZ standards, the time between failures is not regulated for starters, therefore, this indicator can be considered infinite. But they still have to be changed, and this is due to car owners violating operating rules. Car enthusiasts often complain about the quality of starters, pointing out that they are not able to last more than 50,000 km on domestically produced cars. But only a few of them know how to use this device correctly and correctly. Following a few simple recommendations will help you protect yourself from a whole list of starter malfunctions:
- When starting the engine, it is necessary to hold the PU for 10 to 15 seconds; restarting is carried out no earlier than half a minute later. Frequent and continuous operation of the PU leads to systematic overheating of the overrunning clutch, thereby provoking its premature wear. Remember - if there are three consecutive unsuccessful attempts to start the engine, the problem should be looked for in the wiring, fuel equipment or ignition system;
- After starting the engine, immediately turn off the starter, for which you will need to release the key in the lock;
- Many experienced car owners do not recommend using PU when temporarily driving a car (this is what novice drivers often do when the battery is discharged or there is damage to the power supply circuit).
Problems with the starter, ways to solve them on Lada Granta
Often breakdowns are associated with electrical and mechanical components. Therefore, it is important to be able to separate one from the other. Without experience in servicing a technical device, it is better to contact a service center with specialists. Sometimes unprofessional intervention is more likely to harm than restore a good condition.
Electrical
Damage is typical in the area where the current flows from the battery to the starting device (hereinafter referred to as the PU).
- Slow rotation of the rotor, the starter does not start;
- Lack of response when current is supplied to the control unit;
- The control unit clicks, but does not turn: short circuit on the turns, broken wiring, faulty solenoid relay;
- wear of brushes, armatures.
Read also: How to change the battery in a Vesta key
To exclude other breakdowns of adjacent mechanisms, check:
- battery charge level;
- tightness of terminals on the battery;
- electrical wiring in the area from the battery to the starter;
- condition of the ignition switch core.
Mechanical
This type of breakdown is most often caused by malfunctions of the ring, overrunning clutch fork, defects in the flywheel, or pressure spring. Lack of rotation of the crankshaft is the first sign of mechanical failure of the control unit.
If the rotation of the flywheel is accompanied by a characteristic metallic grinding noise, it means the teeth have worn out.
The control unit continues to rotate after the engine starts:
- the return spring burst;
- contact sticking;
- relay is faulty;
- drive shaft deformation;
- damage to the support bearing.
- The starting device starts, but not the first time: the contact board of the traction relay burns out;
- The PU rotates, but with great difficulty: wear of the brush assembly, wear of the bearing;
- Delay in the shaft disengagement: wear of the shaft teeth, bendix.
Types of starters used on Grants
All cars produced in the first years of production of the model were equipped with a starter 21120-3708010-00, which was secured with three nuts. But gradually the manufacturer switched to producing cars with a cable transmission, after which the starter began to be secured with screws. The owner can find out about the type of starter installed on his car by looking at the box, for example:
- boxes 2190 correspond to parts 21120-3708010-00;
- on vehicles equipped with 2181 gearboxes, starters 21901-3708010-00 are installed;
- Jatco automatics correspond to starters 21902-3708010-00.
Instructions for changing the starter on a car with gearbox 2190
First, disconnect the negative terminal from the battery using a 10mm wrench. Then the sensor connector located at the air filter is disconnected and the filter box is removed with pliers from the three mounting points. After removing the box, it is recommended to put it aside; the assembly must be securely fixed using wire for this purpose.
Carrying out dismantling work
The starter module is held in place by studs, and nuts are screwed onto them, but dismantling should not begin by unscrewing them:
- The first thing you need to do is remove the rubber cap, then unscrew the copper nut with a 13mm wrench;
- The next step is to remove the power wire terminal, after which you should disconnect the connector intended for supplying control voltage;
- Next, use a 13mm wrench and unscrew the three nuts securing the starter. Particular attention should be paid to the bottom, most inaccessible nut;
- The part module is then carefully pushed back and removed from the studs. Installation work includes actions similar to dismantling, performed in the opposite sequence.
Instructions for changing the starter on a car with gearbox 2181 or automatic transmission
Initially, you will need to disconnect the battery using a 10mm wrench, then the car will be moved to the inspection hole. Using a size 10 spanner, unscrew the two screws holding the middle shield, after which all nine screws are unscrewed (to solve this problem, use a size 8 spanner).
Next, you will need to remove the middle and left panels, for which you need to unscrew two more screws. However, when changing the starter on sedans with automatic transmission, you can get by by removing only the main shield, which is held in place by eight screws, four of which are located in front, and two more on the left and right sides. They can also be unscrewed using a 8mm spanner.
Lada Largus
Remove the cover (if equipped) of the electronic control unit (ECM) by releasing the two fasteners (flat-head screwdriver). Unscrew the 2 nuts (No. 1) securing the expansion tank (No. 2) (10mm wrench). Remove and move the expansion tank to the side without disconnecting the hoses.
For configurations with JR5 gearbox:
- disconnect the hinges (No. 1) of the gear selection and shift cables from the gearbox (flat-head screwdriver);
- press the clamps on both sides and disconnect the stoppers of the sheaths of the selection and shift cables from the gearbox bracket.
For configurations with JH3 gearbox:
- remove the cover (No. 1) of the gearshift drive rod joint;
- Unscrew the bolt (No. 2) securing the gear shift rod, remove the spacer sleeve and disconnect the rod (10mm wrench).
Unscrew the 3 bolts (No. 1) securing the starter (head “13”).
Raise the car and unscrew the nut (No. 2) securing the bracket (No. 4) to the intake manifold (No. 3) (head “13”). Unscrew the bolt (No. 6) securing the bracket (No. 4) to the cylinder block (No. 5) (head “17”). Remove the bracket (No. 4) that mounts the intake manifold (No. 3).
Unscrew the nut (No. 2), Figure 3-7, and disconnect the harness (No. 1), Figure 3-6, of the ignition system wires from the starter (No. 3) (head “10”).
Unscrew the nut (No. 4), Figure 3-7, securing the starter wire (No. 5) ("10" head). Disconnect the starter wire. Unscrew the nut (No. 3) securing the starter electromagnetic relay wire (No. 5) (head “8”). Remove the starter.
The process is also shown in the video:
Dismantling works
After opening access to the starter, you must perform the following steps:
- First, you should disconnect the control connector, for which the locking tab is lightly pressed;
- Then the rubber cap is moved aside and the nut is unscrewed using a 13mm wrench from the terminal;
- The power terminal is removed, after which the three mounting screws located at the top and bottom are unscrewed with a 13 key.
Note that you need to start with the two lower screws, and the top one should be unscrewed last, while the starter housing must be held, then the housing is carefully tilted back. Installation work is carried out in the reverse order of dismantling.
Components from AvtoVAZ and possible foreign analogues
Initially, KZATE starters were supplied to AvtoVAZ, but since 2011, Valeo has become the main supplier of these parts. For this reason, the current list of components with analogues is as follows:
- Starter 21120-3708010-00 (KATEK, KZATE, ZiT) - they are similar to Fenox ST32101C3 starters;
- Starter 21901-3708010-00 (VALEO) – its analogue is VALEO TS12E901;
- Starter 21902-3708010-00 (VALEO) – similar to VALEO TS12E902.
Do not forget that none of the three options above are interchangeable with the others: the second and third differ in the number of teeth, and elements from KZATE and VALEO are not compatible due to fastenings.