Welcome, friends, to the DIY car repair website. The generator is, without exaggeration, the key component of a car. Its task is to power the entire electrical part of the vehicle while driving (cassette recorder, head light, navigator, and so on).
How to check a generator diode bridge
When the generator fails, the entire load is transferred to the battery. As a result, after just a few hours the car is completely immobilized.
Most car enthusiasts immediately go to a service station, where they spend a lot of money on repairs. Take your time - the problem in 90% of cases lies on the surface.
If you know how to test a generator diode bridge, you can quickly identify the problem, fix it and save money.
How to check the diode bridge of a VAZ generator at home
Most motorists are comfortable with electronics, especially in modern cars; this is not surprising, given the complexity of modern engines.
A large number of different sensors and wiring instills fear in “our brother.” However, there are things that at first glance look very complicated, but in fact their repair and diagnostics are a piece of cake. Today we will talk about how to test a diode bridge with your own hands. saving money and time on a trip to specialists at a car service center. I once wrote about how to repair a VAZ 2101 generator. This time we will talk specifically about the diode bridge, or more precisely about how to check it at home.
It’s probably not worth talking about the role of a generator in a car; everyone knows that this is a very important part, without which one cannot imagine an engine. The service life of the battery largely depends on the performance of the generator. which receives charging from a generator.
A diode bridge consists of four or six diodes that convert alternating current into direct current according to the principle of a bipolar rectification method. The rectifier diodes of the generator play the role of a gateway that allows current to flow in only one direction, preventing current from the vehicle’s on-board electrical network from passing to the stator windings. The diodes are located on the generator body and tend to burn out, there are several reasons for this.
Common causes of diode burnout:
- Ingress of moisture (for example, during engine washing).
- Dust, oil and dirt that can get into the generator while driving.
- When “lighting the car” when the battery is completely discharged, in case you accidentally mixed up “+” and “-“.
In fact, there are a large number of situations in which the diode bridge burns out, but of course we will not describe them.
Let's figure out how to ring the generator diode bridge
Noticing that there are some problems with the diode bridge is not so difficult. It is enough to establish that the battery does not receive sufficient charge or, on the contrary, is overcharged (battery overcharge).
The main task of the generator rectifier diodes is to unidirectionally pass electric current and block its passage back, from the vehicle’s on-board network.
If current passes in both directions or does not pass through the diodes at all, then they are faulty. This happens after unsuccessful “lighting” (confused “+” and “-”), as well as due to moisture getting on the diodes.
So, the test can be carried out either with the bridge removed from the generator or without disassembly (removal). First, let's consider the option of ringing the diodes using a regular 12-volt lamp, without disassembling the generator. To do this, you need to remove the protective casing of the generator and disconnect terminal “B” of the voltage regulator from terminal “30”. You should also disconnect the wires from the regulator terminal “B”. Please note that the 3 diodes marked in red are “plus”, and the 3 diodes with black marks are “minus”.
First of all, all diodes are checked for short circuits: through a lamp we connect the “plus” from the battery to terminal “30”, while the “minus” - to the generator housing. If the lamp is on, the “positive” and “negative” diodes have a short circuit. After this, the negative diodes are checked separately for short circuits. To do this, we connect the “plus” of the battery through the lamp to the mounting bolt of the diode bridge, the “minus” - to the housing. When the lamp glows, this means that there is a short circuit in one or more “negative” diodes.
It is not difficult to identify problems with a diode bridge: this can be seen by the fact that the battery does not receive enough charge or, on the contrary, is overcharged
You need to check the “positive” diodes in a similar way, only now we connect the “minus” to the bolt, and connect the “positive” terminal of the battery to the “30” terminal. As in the previous case, the light of the lamp will signal that there is a short circuit along one or more “positive” diodes.
Additional diodes are “ringed” like this: the “plus” is connected through the lamp to the generator output “61”, and the “-” goes to the diode bridge mounting bolt. The light from the lamp will indicate the presence of a short circuit in one of the additional diodes. In conclusion, we note that it is possible to determine which diode produces a short circuit only after removing the bridge and checking all its elements one by one.
Method number 2 - using a multimeter.
This option will help to identify which (or which) diode is faulty. True, this check can only be carried out by completely dismantling the alternator rectifier unit from the car, so do this first. Next, proceed to the following steps.
- Turn the multimeter into beeper mode. If your device does not have such a mode, set it to 1 kOhm.
- Place the probes against both ends of the diode, then swap them. If in one case the multimeter shows infinity, and in the second - 400-700 Ohms, the diode is working. If both indicators are equal to infinity, then the diode under study is broken; if they have the same or low resistance, it is broken and requires replacement.
- Check all the diodes in this way and you will know exactly which one to solder, which one to replace, which will save you a lot on repairs. Although if you don’t have a great desire – and, by the way, no skills either – then maybe it’s not worth wasting your time. In this case, it would be easier to overpay a little and completely replace the entire diode bridge.
Checking the return current
Diagnostics is carried out with the engine running at high speeds. It is necessary to measure the current consumed by the vehicle components. The probe is pressed against the wire from terminal 30 or B+.
It is necessary to turn on the electrical appliances of the car one by one and record the indicators. The resulting values should be summed. Then you need to turn on all the devices and measure the current indicator. The resulting indicator should be compared with the summed value of previous measurements. The final value should be approximately 5 A below the summed value. A higher value confirms that the node is faulty.
Signs of a diode bridge malfunction
First of all, you need to remember that the diode bridge on the VAZ-2114 is no different from the same unit on the VAZ-2109, VAZ-2110 and other models. Therefore, if you figure out how to determine the malfunction, it will not be difficult to identify it on any of the cars. There are several main symptoms; they can appear together or separately. Any of them requires an immediate check of the generator:
- The warning lamp, which lights up when the ignition is turned on, does not go out even after the engine is started. This is a general indicator of a problem, but if the diode bridge has failed, the lamp will light in any case. If a voltmeter is installed in the car, you can check its readings; the arrow will most likely be either in the red zone or at its very border.
- Another option is that the warning light does not light up when you turn the ignition key and does not light up after starting the engine.
- When measuring the voltage produced by the generator with the engine running, the reading is less than 13.5 Volts. You need to measure at the battery terminals.
- The next morning the car will not start due to a dead battery, although in the evening it was in normal condition. After charging the battery, it discharged again in a short time, and the generator housing becomes so hot that you can burn your hand on its surface.
- Extraneous noise appears under the hood, most often it is a whistle or howl. The noise level may vary depending on engine speed.
- Various errors appear - the ABS, ESP, and so on may light up. The power steering may stop working, the radio will begin to wheeze and freeze. Instead of a turn signal, the light turns on. All this manifests itself against the background of a dead battery, which does not charge due to a broken diode bridge.
- The headlights begin to dim or stop working altogether, and the air conditioner does not cool as it should.
These are the main signs of a diode bridge breakdown, but it is worth remembering that they may indicate other generator failures. Therefore, first of all, you need to accurately identify the faulty unit. It is not necessary to take the car to a service center for diagnostics; the car owner can do the work; a minimum set of tools is needed.
Advice!
If the control light on the panel lights up or, conversely, does not work, first of all you need to check it and the control relay. Often it is these elements that are faulty, and not the generator.
Why does the diode bridge burn out?
There are several reasons for the failure of the diode bridge on VAZ cars. To prevent the breakdown from occurring again, you need to check the machine for one of the options described below. Only by eliminating the problem can normal operation be ensured.
Most often, a bridge burns down due to the following:
- Moisture getting inside the generator housing. Over time, casings or connections may become loose, which allows water to enter. Also, diodes burn out due to contaminants: soot, lubricant particles, which inevitably accumulate inside the generator over time.
- A faulty battery can also cause diodes to burn out. Another very common option is when car enthusiasts confuse the positive and negative terminals on the battery when connecting. In this case, the diode bridge almost always burns out.
- If the car is from another car in violation of the rules of this process, the diodes may also burn out.
The diode bridge, like any spare part, has its own service life. It usually lasts about 10 years, after which the unit may fail due to normal wear and tear.
It is best to periodically diagnose the car, check the serviceability of the main components and conduct an inspection to identify problems when they are not yet fatal. It is recommended to check the battery annually and measure the charge level to monitor the condition of the generator.
How to determine generator malfunctions
Signs of a faulty generator diode bridge. A car generator and a generator, a household power station are similar. Accordingly, the principles of troubleshooting and repair are the same. The only difference is that the car generator contains a rectifier and a voltage regulator, so the car network is designed for 12 Volts. The article discusses generator malfunctions and how you can fix them yourself. Your vehicle is equipped with a warning light that can alert you that the alternator has lost power. If this happens, you need to make sure that the sensor is working and the lamp is connected correctly.
It often happens that these lamps use a bad connector or the control relay fails. It is also possible that your battery, charging terminals are faulty, or it is simply discharged. When there is a lot of energy consumption, for example, when using lighting devices to the maximum, charging, or leaving the radio on overnight. Generator malfunctions may occur due to increased energy production when the voltage is above 14-15 Volts. The numbers vary depending on the model.
Therefore, if the battery breaks down, you should always check the generator too. Sometimes the generator begins to deliver current below the required limit of 13.2 Volts, then it is urgently necessary to check it for damage.
Before removing the generator, it is necessary to check the tension of the drive belt. Lack of electrically conductive connections between the battery or generator and the car body; voltage may be lost “on the way” to the battery. Also check the bearings for clearances and the integrity of the fuses.
For some types of faults there is no need to remove the generator. If there are knocks or noise during work, it is necessary to disconnect the wires: the noise will disappear - but a short circuit will form, unfortunately, these are expensive repairs, their cost exceeds the price of new equipment.
The noise remains - replace the bearings, they have worn out during use. Check the brushes, maybe it's time to replace them too. The contact brushes and rings may not be pressed well, then the spring should be adjusted. Get rid of dirt and burnt marks on the rings, if any. Sandpaper is the best way to remove scorch marks. If the rings become unusable, the rotor must be replaced. Check the rotor contacts with a multimeter.
Generator malfunctions in the form of a damaged rotor must be removed in the following order. Since a faulty rotor cannot be replaced, it must be completely replaced if it fails. The same applies to the stator. Remember that the rotor and stator must not have electrical contact with the body or other parts of the vehicle. A faulty stator must be replaced. Voltage rectifier diodes should not conduct current in both directions.
How to change a diode bridge in a generator
Changing the diode bridge in the generator
To perform the work you need to acquire:
- a set of heads;
- flat screwdriver;
- curly screwdriver;
- new diode bridge.
Note! Basically, the generator stops charging the battery due to a faulty voltage regulator or breakdown of the diode bridge. For more detailed diagnostics, it is recommended to remove the device from the engine compartment and install it on a plumbing installation.
Replacement of the bridge must be carried out in a certain sequence:
- After removing the diode bridge, check the current flow in the circuit. This can be done using an ohmmeter or a special tester. If the semiconductors fail, the bridge will need to be replaced completely.
Note! It is difficult to replace individual parts of the bridge yourself; this requires certain skills.
- To reach the diode mounts, you need to remove the brush block from the generator. The bolts that hold the back and front covers are unscrewed. One part of the device is removed from the stator.
- Half of the generator is set aside. Using a socket wrench, unscrew the nuts securing the stator winding leads to the rectifier unit. The middle area of the device will be disconnected only after the negative wire is detached from ground. Also, the bolts with the corresponding insulators and the diode bridge itself are removed from the back cover.
- The new diode bridge is installed in its place. Now bolts with insulators are placed in the cover, the winding terminals are put on them and tightened with nuts.
- The rotor and front cover are installed into the rear through the stator. The generator housing is tightened using bolts. At the last stage of work, brushes are installed.
As you can see, the process of changing the diode bridge is not complicated; it is recommended to watch videos and photos to do the work yourself. In addition, the novice car mechanic is provided with additional instructions with a detailed description of the processes. Since the price of service stations is not acceptable for everyone, many try to repair their car themselves.
Check Features
When checking the generator of a VAZ 2110, 2107 and others for serviceability, the following conditions must be met:
- An accurate multimeter should be used for diagnosis.
- The normal voltage is 12 V.
- If it is necessary to replace the wiring, you must use wires with the same cross-section as the original.
- Before checking, you should check that all fasteners are connected correctly and the belt tension is correct. If necessary, the connections should be adjusted to normal, the belt should be loosened or tightened.
During the verification process it is prohibited:
- short circuit the wires;
- connect terminals that differ in purpose and parameters, connect terminal 30 or B+ to ground;
- diagnose a generator without connected consumers.
Signs of generator malfunction and ways to eliminate them
The operation of the generator is controlled by a signaling device on the instrument panel. When the ignition is turned on, the window should light up and go out after the engine starts. If this happens, then everything is fine, the generator is working.
Too bright or too weak illumination of the indicator already indicates certain malfunctions of the generator system parts. In any case, insufficient battery charge always indirectly indicates problems with the generator.
The generator does not supply charging current at all
A very common occurrence is low drive belt tension. When it slips, the generator cannot operate at full capacity, and this leads to a gradual discharge of the battery. Belt slipping can also be caused by worn alternator bearings. It must be remembered that the service life of this unit is less than that of the engine, and is about 130-160 thousand km.
If the drive belt tension is weak, the generator cannot operate at full power, which leads to a gradual discharge of the battery
Brush sticking, the second most common problem, is caused by dirt buildup on the brush holder and brushes themselves, as well as weakened brush springs. To solve the problem, it is necessary to clean the above elements and, accordingly, replace the springs with new ones. However, serious wear of the brushes may occur, which will require their replacement.
During intensive use, sometimes the so-called burning of slip rings occurs, as a result of which contact with the generator significantly deteriorates or disappears. This problem can be solved by thoroughly cleaning and grinding the rings or turning them. Additionally, it is worth inspecting the wiring connecting the generator and the battery for breaks.
Also, the reason for the lack of charging current may be a faulty voltage regulator, which must be replaced with a new one. There are frequent cases of breakage of the excitation winding; with some experience in repair work, this can be eliminated
It is also important to pay attention to the fact that there are cases of the rotor touching the surfaces surrounding it. This may lead to partial damage. The cause is usually worn out bearings or seating areas.
The cause is usually worn out bearings or seating areas.
When charging current is supplied, but the battery does not charge normally
Often the battery does not take a charge due to poor contact of the “ground” of the generator itself with the “ground” of the voltage regulator
This state of affairs may be a consequence of poor contact of the “ground” of the generator itself with the “ground” of the voltage regulator. Therefore, you need to check the reliability of the wire, as well as the tightness of the contacts. There may be a short to ground in the generator excitation circuit, which triggers the voltage regulator protection relay. It is necessary to find the location of the short circuit and fix the problem.
Checking the generator on the car
First of all, you need to see if the alternator belt is intact. If it is not torn, then the belt tension is checked. Then it's time for the battery. Using a tester (multimeter), we measure the voltage at the terminals. It should be around 12−12.7 volts. If everything is fine, start the engine. If the battery is discharged, charge it and start the engine again.
We measure the voltage at the battery terminals. It should be within specified limits, usually from 13.2 to 14.5 volts. But on modern cars these limits may differ. If you have an instruction manual, you can read it. Deviation from the specified values in any direction is a malfunction. These deviations can be of three types:
- Lack of charging current - the generator does not work.
- There is a charging current, but below the minimum value -
- Voltage above the maximum value means the battery is overcharged.
All three cases indicate an existing malfunction in the vehicle's electrical supply system. it is necessary to carry out a comprehensive check of the generator.
But before that, conduct a visual inspection of all the wires and cables that go from the generator to the battery. There should be no visible damage, breaks or oxidation of the electrical wiring. Be sure to check the terminals on the battery, starter and alternator. They must be clean and dry. Any oxidation, rust or dirt must be cleaned off. Often this helps restore lost contact and the car begins to work as expected. If this does not help, we proceed to a detailed check.
Using a Multimeter
For further inspection, it is better to remove the generator from the car. First of all, remove the relay regulator from the generator and check it. To check the voltage stabilizer, you will need a multimeter and a charger with regulated voltage. It would be better to use a power supply instead of a charger. Voltage adjustment from 0 to 16 volts will be sufficient.
Connect the plus of the power supply to the regulator - usually this is a male plug connection. Hook the minus to the minus, it is usually output to the ear of the relay mount. Connect the red wire of the tester to the positive wire of the power supply, the black wire to the negative wire. Connect two stripped wires to the brushes, one for each. A light bulb is connected to the other pre-stripped ends (it can be removed from the rear lights of the car during testing). The test bench is ready.
Continuity of the relay regulator
Connect the power supply to the network, carefully use the regulator knob to begin raising the voltage. At the same time, monitor the multimeter readings. The light bulb should not light up at the very beginning, but as the voltage rises it should light up, first at half-incandescence and as the voltage increases, the brightness should increase.
When the 14.5 volt mark is reached, the regulator should operate, cutting off the voltage. The light should then go out. It is generally accepted that the stabilizer is working if it cuts off the current at values from 14.2 to 14.8 volts. If this happens at lower or higher values, then the voltage regulator is faulty. The relay is also faulty if there is no current cutoff at all.
How to check the generator on a VAZ-2109 yourself
The generator in the car provides the generation of electricity through the power plant.
If it breaks, then first of all the battery runs out, and as a result the car simply cannot move. This article tells you how to check with your own hands the generator installed on a VAZ-2109 car.
It is worth noting that it makes no difference which engine is installed on the car - an injector or a carburetor. In both cases, diagnosis is made using the same algorithm.
In order to determine the nature of the breakdown at home, you first need to know how to diagnose the generator.
The first stage is carried out without removing the device from the machine. There are several options, but the best quality is a multimeter. True, for this it is best to involve someone you know.
First of all, you need to find out whether the voltage regulator is capable of doing its job. Experts note that most often it is because of this that the generator may not function properly. The problem with it arises due to excessive voltage in the electrical network.
The generator itself is tested like this:
- set the multimeter to volts;
- start the power unit;
- measure the voltage at the battery and at the generator terminals.
Normally, the device will show from 14 to 14.2 volts. After this, you will need to depress the gas pedal - the voltage increase should not exceed half a volt in this case.
An increase in this indicator indicates that the generator’s performance is impaired. Most likely, the voltage relay will need to be replaced.
Alternatively, you can also do this:
- start the engine and let it run for a while;
- press the gas and bring the crankshaft to 3 thousand revolutions;
- turn on the headlights (high beam);
- heated rear window;
- stove fan.
With such a load, the battery voltage should be more than:
- 13.2 volts (generator type – 9402.3701);
- 13,6 (37.3701).
Indicators different from normative ones indicate:
- winding faults;
- failure of the voltage regulator;
- brush breakage.
To exclude the regulator from the list, you need to de-energize all devices except the headlights and measure the voltage again. If the specified node is serviceable, then the indicators will be as follows:
- for 37.3701 – up to 14.6;
- for 9402.3701 – up to 14.7.
Replacing the generator diode bridge on a VAZ 2110, VAZ 2111, VAZ 2112
Welcome! Diode bridge - it gives a charge and gives it an even charge (the generator gives a jumping charge, and this bridge straightens it) to the battery when the car starts and the generator starts working, which is why when the diode bridge fails, the battery is immediately discharged and upon arrival one day day in the car, the car cannot really start and you have to push it, or take it on a cable, one thing is good, when the diode bridge fails, the battery charge lamp on the instrument panel will immediately notify you about this, and if a person knows even a little about cars , then he will already understand what happened and in the near future he will drive the car to a service or to a garage and in the garage, checking the generator brushes, determine whether the diode bridge has become unusable or the brushes and, if necessary, replace the worn part with a new one.
Note! To replace the diode bridge with a new one, you will need to stock up on: All the keys that are present in your set and screwdrivers, but if you want to check the old diode bridge for functionality, then take a multi-meter (And we recommend that you check it)!
Summary:
Where is the diode bridge located in the generator? Let's start with the fact that cars of the tenth family were equipped with different engines, different body kits (We are talking about the VAZ 2112 coupe) and, accordingly, such parts as a generator, depending on the engine, were also different, but in the injection system, with an 8-valve engine, one type of generators, with 16 valves, is completely different, carburetors also had their own generator, usually 55 amperes, because in carburetor cars there are many times less electronics and they only needed the generator that was installed on them, well, in this article we will only analyze one generator, marked 9402.3701 (It was used on fuel-injected 8-valve cars), the photo below shows just such a generator, it is very easy to disassemble, as you can see, the cover of such a generator is not secured with bolts but simply with latches (indicated by red arrows) By bending these latches, you can easily remove the cover and see behind it the diode bridge, which can be seen very clearly in the small photo.
Note! As for the generator marked 37.3701, which was used in carburetor eight and nine engines (later they began to install these engines on dozens, this generator migrated to them too, like the engine itself), it looks completely different and produces clearly less amperes (55 amperes, against 80 or some even go to 90, the latter, by the way, are absolutely identical in appearance to 80 amps and are even interchangeable, so if you are the owner of an 8-valve injection engine, you can install a generator with a little more amperes if 80 is not enough for you and the installation will be absolutely identical) but this is enough for the carburetor, the diode bridge in such generators is also not difficult to replace, you just need additional tools and more time, and also care is needed, because if the generator is not assembled correctly, then it can short-circuit and damage the wires that The batteries go and the battery itself will burn, so be extremely careful and attentive when assembling the generator in the car! (How to replace the diode bridge on a carburetor, read the article: “Repairing a generator on nines”)
When do you need to change the diode bridge in the generator? 1. Only by checking it can you find out whether the diode bridge can be replaced or whether it will last a long time, it is checked only with the generator removed, so as soon as you remove the generator, remove the plastic cover from it and the bridge itself, so that it is convenient to work with it and hold it, after all the operations done, turn on the multi-meter as shown in the photo below (It needs to be turned on in ohmmeter mode) and connect to the diode bridge, namely to the common bus of auxiliary diodes (Number 1) a red probe, and the other, black , to the terminal of the diode (Number 2) that you want to check (You need to check all the diodes, so connect the black wire in order and just always remember, the diode should not pass current, if this suddenly happens, the multi-meter will immediately show infinity and this will indicate that the diode bridge is faulty and needs to be replaced).
Note! Let us explain to you what infinity is, it’s just that not everyone knows it, in general, infinity is indicated differently on different testers, for some it simply does not react (For example, it was 0, and it still stands after connecting the probes coming from the tester), while for others the tester shows 1 and stands firmly on this number (In this case, the readings should not move, that is, before connecting the tester showed 1 and after connecting also 1, this is infinity, but if it happened that it showed 0 and after connecting 1, this is already indicates that the diode being tested has resistance), but if there is suddenly resistance, then the tester will definitely have to show the result (see photo 2 above), if in your case this happened with all the diodes being tested, then your bridge is not subject to replace with a new one!
2. The second, final test, the black probe is connected to the plate of the generator rectifier block, inside which is the diode that you are going to check, and the other, red probe, is connected to the terminal of the diode itself, a working diode should not pass current and thus the tester will not should give a value of infinity, then swap both probes (see photo 2) and the tester will definitely have to give some value of several hundred, if everything turned out exactly the same for you, then the diode bridge is working and what else is the problem (B stator for example or in brushes).
Malfunctions of the VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 generator
The generator is responsible for power supply to the entire on-board network of the car with the engine running. Signs of a malfunction of the generator of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
After starting the engine, the battery discharge indicator lamp in the instrument panel lights up
The generator does not produce the required charging current. Simultaneously with the light on, the voltmeter readings tend to zero. The battery is constantly not recharged. Using a voltmeter (multimeter), we check the voltage at the battery terminals (the engine is idling). The voltmeter readings should be as follows: generator 37.3701 - 13.6 V, generator 9402.3701 - 13.2 V.
The “folk” method of checking a generator by removing the terminal from the battery while the engine is running is only suitable for carburetor engines. If the engine stalls after removing the terminal, it means the generator has stopped producing electric current.
If it is less, then the problem is not in the faulty wiring going to the control lamp and voltmeter, but in the generator. Next, sequentially, from simple to complex, from the most probable to the least probable, we look for the cause of the malfunction.
— The generator drive belt tension is loose
The belt slips on the pulley, and the generator rotor stops rotating at the required frequency. In this case, a “whistle” from the generator drive is possible. We check and adjust the belt tension if necessary.
— The generator voltage regulator is faulty
There may be a short circuit between its terminals “B” (“D+”), “W” (“DF”) or “stuck” (the brushes of the brush assembly have worn out). The easiest way to check the voltage regulator is to install a known good one. We replace the faulty regulator with a new one. Read more: “Checking the generator voltage regulator for VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars.”
— The diode bridge (rectifier unit) of the generator is faulty
Most likely there is a “break” in its valves or a short circuit in the negative valves. The power diodes of the excitation winding may also be damaged. The diode bridge can be checked using an ohmmeter (multimeter in ohmmeter mode) both directly on the car and on a removed generator.
Checking the diode bridge of the generator of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— The generator stator is faulty
“Open” or short circuit in the stator winding. We check the stator with an ohmmeter, and if there is a malfunction, replace it with a new one.
checking the stator windings of generator 37.3701 for “break”
— The generator rotor is faulty
Perhaps the leads of the excitation winding located on the rotor have become detached from the contact rings to which the brushes are pressed. We check the rotor and replace it with a new one if necessary.
generator winding terminals 37.3701 for VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
The battery is recharged and “boils”
The generator produces too much charging current, higher: generator 37.3701 - 14.6 V, generator 9402.3701 - 14.7 V, which is checked with a voltmeter at the battery terminals. The needle on the standard voltmeter is in the red zone at the end of the scale.
— The voltage regulator is faulty
Most likely there is a short circuit between its terminal “Ш” (“DF”) and “ground”. Replace the voltage regulator with a new one or a known good one.
The generator makes noise or “howls” when operating
The nut securing the generator pulley has come loose, the generator bearings are worn out, there is an interturn short circuit or a short circuit to ground in the stator winding (the generator “howls”), a short circuit in one of the generator valves.
Notes and additions
— The causes of such malfunctions as: the warning lamp does not light up after turning the key in the ignition switch and starting the engine (the standard voltmeter shows normal voltage) or the lamp does not light up and the voltmeter does not work (or the control devices do not work completely) are not a malfunction of the generator, but a burnout of the control panel lamp, a break in its power supply circuit, a blown fuse No. 5 (F16) in the mounting block (responsible for supplying current to the excitation winding of the generator), a break in the power supply circuit of the instrument cluster (orange and orange-blue wires), a malfunction of the ignition switch.
— If the discharge warning lamp lights up at idle, and goes out when you press the gas pedal and while driving, you must first check the tension of the generator drive belt, and if that doesn’t help, then the problem is most likely in the additional resistors located in the relay mounting block and fuses. If they fail, the generator is not excited at low speeds, and therefore does not charge. It is necessary to either completely change the mounting block, or unsolder additional resistors and replace them with new ones.
More articles on generators for VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
Diagnostic methods
There are two main methods that will allow you to determine the malfunction of the generator diode bridge. You need to choose based on what you have at hand. The first option requires the presence of a multimeter, and the most entry-level option, which is inexpensive, is suitable. The second is a regular 12V light bulb with three long wires so you can connect them to the right pins.
Diagnostics using a multimeter
Let's look at the option without removing the diode bridge, since it requires less time. The test is easy to carry out on an installed unit if you know the main features. The process is simple; you first need to provide access to the generator contacts. After this, carry out the following checks:
- When checking for a short circuit, press the positive contact of the multimeter to pin 30, and the negative contact to the body. If everything is in order with the diode bridge, the resistance readings will tend to infinity. Any other reading indicates a problem.
- To find out whether the positive diodes are broken, you should attach the positive terminal to pin 30 on the generator, and the negative terminal to the diode bridge mounting bolt. If everything is in order, the resistance will tend to infinity.
- To test the performance of negative diodes, you need to press the positive probe against the bolt that secures the diode bridge, and attach the negative probe to the housing. The readings should tend to infinity.
- To check additional diodes, the positive contact of the multimeter should be pressed to pin 61 on the generator, and the negative contact to the mounting bolt of the diode bridge. As in all cases above, the resistance should tend to infinity.
Important! Do not forget to first switch the device to ohmmeter mode.
Using simple recommendations, you can literally check in a few minutes and find out whether the diode bridge has burned out or the reason lies in another unit. You can use not only a multimeter, but also any other device if it has an ohmmeter mode.
Checking the bridge with a light bulb
This option is especially good on the road, because it only requires a 12-volt light bulb and three long wires with bare ends. Or you can use a ready-made warning lamp, they are sold in car dealerships. In this case, proceed like this:
- To detect a short circuit, the plus must be pressed to pin 30 on the generator, and the minus must be shorted to the housing. If the light is on, you need to change the diode bridge, but if not, then everything is in order.
- To test positive diodes, you need to apply positive from the battery through the light bulb to pin 30 of the generator. Connect the negative from the battery to the bridge mounting bolt; if the lamp is on, one or more positive diodes are broken.
- From the battery through the light bulb, the plus is given to the diode bridge mounting bolt, and the minus goes to the housing (also from the battery). If the lamp is on, the negative diodes are faulty.
- If you connect the 61 terminals of the generator to the positive terminal of the battery through a light bulb, and apply the negative terminal to the diode bridge mounting bolt, you can check additional diodes. If they are faulty, the lamp will light up.
This option, due to its simplicity, allows for quick diagnosis. However, it will not require much time and will allow you to identify the problem within a few minutes. But it is better to work with an assistant to hold the wires.
Signs and Symptoms of a Malfunctioning Alternator Overrun Clutch
The generator overrunning clutch is a mechanism that dampens shocks from the pulsating rotation of the crankshaft in time with the power stroke of the piston. Installed on a number of cars that have additional units, for example, an air conditioning compressor.
The main symptoms of the malfunction are vibration and rattling felt inside the car when the air conditioning compressor is turned on. This symptom most often occurs if the car is in gear, the brake is pressed, or it is moving slowly.
The simplest and most accessible way to diagnose an overrunning clutch is to raise the speed to 3000-4000 and turn off the engine. If the clutch is working correctly, you can hear a delayed sound, reminiscent of a turbine stopping due to inertia. If you have an assistant, it is visually possible to see the inertial rotation of the generator when the drive belt of additional units comes to a complete stop.
The practical part is removing the generator, disassembling it, repairing it and reinstalling it.
Due to the fact that the generator is located under the hood of the car, it is necessary to turn off the engine, turn the steering wheel to the right all the way and open the hood. The electric generator on VAZ 2108 - 15 cars is installed in front of the engine, in the lower left corner of the engine compartment, between the engine and the cooling radiator.
Before dismantling the generator, it is necessary to disconnect the ground from the battery, i.e. negative contact.
Replacing VAZ generator brushes
Before removing the generator itself, in order not to do unnecessary work, we remove the charging relay from the generator housing and check the production of the generator brushes. The charging relay is installed in the rear of the generator housing, and is attached to it with two bolts. To unscrew them you will need a Phillips screwdriver. When unscrewing the bolts, be careful not to drop them on the crankcase guard, otherwise getting them out of there will be one big problem. To remove the relay, you need to disconnect the wire, the “female” contact. After removing the charging relay and visually inspecting the brushes, we decide to purchase a new generator voltage regulator relay or reinstall the dismantled one, depending on the wear of the brushes. For their normal operation, a brush length of at least 4 cm is required. Now we proceed directly to removing the electric generator from the engine.
- We disconnect the wires from the generator - as a rule, they are red and consist of two groups of wires, red. One group consists of two wires and is attached with a nut to a bolt on the rear wall of the generator. The other group consists of one wire and is connected to the generator terminal via a male-female contact, also on the rear wall of the generator.
- To remove the generator from the engine, you need to unscrew two nuts and one bolt in the following sequence: unscrew the nut attached to the generator belt tensioner bar (at the top of the generator), unscrew the bolt securing the tensioner bar to the engine block and remove it. The last step is to unscrew the nut from the bolt securing the generator bracket to the engine block.
- The generator mounting bolt should be pushed to the left, out of the bracket, until it stops against the body shell or the generator’s mud protection.
- On the right wheel side, you need to unscrew the two screws that secure the dust protection of the generator to the car body.
- If the generator mounting bolt still rests against any body parts, you should press on the engine with one hand, and at the same time pull out the bolt with the other hand.
Now your generator is completely disconnected from the engine, and you can begin to disassemble and repair it.
Disassembling the electric generator
When disassembling an electric generator, you need to have two important things on hand: a bearing puller and a vice. This will greatly simplify and speed up your work. Using a wrench set to “19”, unscrew the nut from the rotor shaft, which secures the impeller to the shaft.
To do this, you need to hold the impeller directly with one hand and unscrew the nut with the other hand, counterclockwise. It will take some effort, of course, but this nut needs to be unscrewed. The generator impeller is secured to the shaft with a key, and after removing the impeller from the shaft, it is necessary to remove this very key.
Now we turn the generator over with the back cover up, and unscrew the four nuts with an “8” wrench. We take out the released four studs and release the front part of the generator housing.
In the front part of the generator cover there is a “front” bearing secured by plates. We remove it by unscrewing the nuts and plates and knock the bearing out of its seat. The easiest way to do this is with a wooden plank, the size of which matches the diameter of the bearing.
Now we need a vice: screw a nut onto the rotor shaft and secure the generator, or something that we have not yet disassembled, in the vice. We tear off the back cover with a sharp upward movement from the bearing seat.
VAZ-2107. No battery charging. Generator repair.
Reasons for the battery not charging.
Diagnostics and repair of Generator VAZ, Gazelle, Volga, Sable, Lada, Priora
The generator circuit with additional diodes has the following properties
1. Allows you to conduct excitation current directly inside the generator bypassing the ignition switch contacts
2. The excitation circuit with additional diodes is separated from the battery by a light bulb, this reduces the initial excitation current and eliminates rapid discharge of the battery if the engine does not start and the ignition is on.
3. When starting the engine, a very small excitation current passes into the generator through the bulb, so the generator rotates very easily, which facilitates the operation of the starter.
4. A light bulb in the excitation circuit limits the initial excitation current and allows you to control the operation of the generator
Now in more detail
Cars use a three-phase synchronous alternating current generator.
Electrical equipment requires direct current to operate, so a rectifier must be installed in the generator. The three-phase generator rectifier is a diode bridge
according to Larionov's scheme. - Three arms of two diodes each
Such diode bridges were used on early types of generators for Moskvich, Zil 130, Zhiguli cars.
A simple diode bridge on a Zhiguli without additional diodes
Any car alternator works in tandem with a voltage regulator. The regulator maintains a given generator voltage level. An excitation current passes through the voltage regulator, which creates a magnetic field in the rotor. When the rotor rotates, a change occurs in the magnetic field crossing the generator winding, which generates an EMF in the generator winding.
Early generators used the simplest transistor voltage regulator
Let's look at the diagram
To excite the generator, you first need to supply it with current from the battery. When the ignition is turned on, this current flows from the battery, through the rectifier output point and further, through the brushes into the field winding. When the generator is excited, it itself becomes a source and begins to charge the battery and power all the loads. The generator transfers part of its current to its own excitation. The excitation current goes through the ignition switch
The excitation current of a powerful generator reaches 5 Amps, this is a fairly large current that heats the wires and loads, and when opened, creates a strong spark. All excitation current passes through the ignition switch contacts, and the contacts gradually burn out. This reduces the reliability of the ignition switch - battery charging deteriorates and the stability of the ignition system is disrupted. It is necessary to ensure that the excitation current does not pass through the ignition switch. The excitation winding can be powered directly in the generator if part of the current in the windings is diverted through additional diodes.
As experience was gained in using first-generation alternating current generators, such a problem emerged. The battery turned out to be discharged, unexpectedly for the driver. The reason was that the ignition switch, forgotten or accidentally left on, kept the generator excitation circuit on and the battery was discharged through the excitation winding with a current of 3-5 amperes. For a not very new and, as usual, not fully charged battery, 2-3 hours is enough and the battery could no longer start the engine. This phenomenon was explained by the fact that for the initial excitation of the generator when starting the engine, the excitation winding was powered from the battery through the ignition switch. If the ignition switch is turned off, there was no problem. But once or twice a year, many drivers did not turn off the ignition for various reasons.
The use of additional diodes and preliminary excitation through a light bulb made it possible to solve this problem.
The battery, as before, was necessary for the initial excitation, but a light bulb was included in the excitation circuit, which greatly limited the excitation current at 100 milliamps, this was enough to initially excite the generator, but to operate the generator at full power, a large excitation current is already needed - approximately 5 Amperes.
In such a generator circuit - with a light bulb in the excitation circuit, the operating excitation current is supplied to the rotor from an additional rectifier, which is not connected to the battery, therefore, if the engine was not running, leaving the ignition switch on did not lead to rapid discharge of the battery, since There were light bulbs in the path of the discharge current and greatly limited the current.
Only the initial excitation current, limited by the light bulb, passes through the ignition switch, this relieves the ignition switch contacts and makes the charging system more reliable.
The light bulb becomes a very convenient indicator of the charging process. If it lights up while the engine is running, it means the generator is not charging the battery.
Thus, the point of using additional diodes to power the generator excitation winding is to ensure that the generator excitation current is taken directly from the generator and does not pass through the ignition switch, and so that the battery does not unexpectedly discharge if the ignition switch is left on when the engine is not running.
Another important advantage of a generator circuit with additional diodes:
When starting the engine in a circuit without additional diodes, a large excitation current immediately flows from the battery, the generator is fully excited and strongly resists the rotation of the starter.
In the circuit with a light bulb, the initial excitation current is small and it is easy to turn the generator; it is fully excited after the starter is turned off, which makes starting the engine much easier.
The circuit with additional diodes was widely used by all generator manufacturers in the 80s and 90s, and to this day, generators using this circuit are produced for cars of previous years.
For modern generators, a circuit with additional diodes is not used. Diode bridges with additional diodes are only available for generators designed in the past.
In modern generators, more complex voltage regulators with microcontrollers are used; they allow you to accurately regulate the voltage, relieve the ignition switch, protect the battery from discharge, and facilitate the operation of the starter when starting. (See the article “S IG L Denso Toyota Generators.”) and provide advanced generator diagnostic functions.
This type of generator includes the latest generation of Russian generators without additional diodes with a multifunctional voltage regulator.
These are generators for Chevy Niva, Kalina, Grant and all subsequent VAZ models, as well as the most modern generators for GAZ and KAMAZ
— .
Currently, three generations of diode bridges are produced. For older generators without additional diodes, for mid-generation generators with additional diodes and for modern generators, again without additional diodes.
If the diode bridges are structurally the same, then for old generators it is quite possible to use a diode bridge with additional. diodes, and about additional You just need to forget the diodes.
You can use it the other way around, everything will work, the light bulb will have to be bypassed, that is, restore the old circuit, just don’t forget to turn off the ignition if the engine doesn’t work.
For many modern generators, diode bridges without additional diodes have a design derived from the previous one with additional diodes (compare BVO 3 -105-01 and BVO 4-105-01, see the last figure) so they are fully compatible in size and mounting locations.
An old diode bridge with additional diodes can be safely installed in a more modern generator (9402.3701-03 without additional diodes), but the voltage regulator must also be installed of the old type (778.3702). You can also install it with a new regulator (845.3702), just do not connect additional diodes, but you will have to make an additional phase output for the multifunctional voltage regulator to operate and connect the second output of the regulator to the positive output of the diode bridge.. You can also install it the other way around. If there is a diode bridge without additional diodes, it can be installed in an old generator (9402.3701), but you need to either solder an additional one. diodes, or choose a voltage regulator that works with phase control (845. 3702). External wiring does not require modifications.
Diode bridges with additional diodes may have an additional terminal connected to the phase. It is needed for very early generators that were installed on Volgas and Gazelles, with tachometers that, like diesel cars, were powered by a generator. These diode bridges can be safely installed on more modern generators.
To power consumers in the vehicle's on-board network and the excitation winding of the generator itself during engine operation, a constant voltage electric current is required.
The function of converting alternating current induced in the stator winding of the generator into direct voltage electric current is performed by its rectifier unit (diode bridge).
Diode bridge location
As standard, the rectifier unit is located at the rear of the generator. For example, on the 37.3701 generator it is attached to the rear wall of its rear cover.
Generator diode bridge design
Using the example of the rectifier unit BPV56-65-01 of generator 37.3701 of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars.
The rectifier unit consists of two aluminum heat-removing plates, which are combined into a whole structure through three insulating sleeves using rivets. One plate (lower) is connected to the “ground”, through the generator housing, the other (upper) to the “plus”, through the terminals of the stator windings. The positive plate has three contacts for connecting the terminals of the stator windings and a terminal through which voltage is supplied to consumers (terminal “30”).
Three diodes are soldered into each of the plates, i.e. three positive diodes (D104-20) and three negative (D104-20X), designed for a current of no more than 20A. Positive and negative diodes are combined in pairs. In addition, there are three additional diodes (KD223A) rated at 2A. They are mounted on a plastic holder and power the generator excitation winding. The main and additional diodes are combined into a common bus, which has a plug terminal on one side (pin 61 of the generator) and a terminal for the voltage regulator on the other side.
Operating principle of a generator diode bridge
The operating principle of a diode bridge is based on the property of diodes to pass electric current in only one direction. Electric current enters the diode bridge through the terminals of the stator windings attached to it. It flows through the diodes in one direction. But no way back. Therefore, the current is constant (rectified).
Malfunctions of the generator rectifier unit
There are only two main faults: “break” and “short circuit” of the diodes. If there is a “break”, the diode stops passing electric current; if there is a “short circuit”, the current flows in both directions - the diode is “broken”. More details:
“Checking the diode bridge on a generator removed from the engine,”
“Checking the diode bridge of the generator without removing it from the engine.”
Applicability of rectifier units on VAZ cars
— Generator 37.3701 – rectifier units with two outputs (before 1996 of manufacture): BPV-56-65-01, BPV-56-65-02B, with one output (terminal “61” on the bridge body): BPV-56-65 -02G.
Notes and additions
— Electric current of alternating voltage is a current that changes in magnitude and direction at regular intervals.
— Electric current of constant voltage is a current that does not change in magnitude and direction throughout the entire time.
— Diode (semiconductor) – an electronic device consisting of silicon or magnesium wafers with certain properties. If you connect a “plus” to its positive terminal (anode) and a “minus” to its negative terminal (cathode), then an electric current will flow through it in one direction (the diode is open). If the polarity is reversed, then the current will not pass (the diode is closed).
More articles on car generator
— Operating principle of a car generator
— Complete disassembly of generator 37.3701 of VAZ 2108, 2109, 21099 cars
— Checking the health of the generator
— I found the generator voltage regulator, what to do?
— Checking the generator stator
FUNCTIONAL PURPOSE AND FEATURES OF THE RECTIFIER
The diode bridge of the generator, depending on the type, can consist of either 4 or 6 diodes that perform the function of converting alternating current into direct current with a given pulsation frequency. The operating principle of the device is based on the bipolar rectification method, which is also widely used in a variety of electronic systems.
In addition to the conversion, the unit acts as a valve, the purpose of which is to pass current exclusively in one direction. With a properly functioning device, the current from the generator enters the fourteenth power network, but does not pass back to the stator. If the node fails, current leaks and flows in both directions. This will cause a constant lack of power, and the vehicle's systems that consume electricity will not be able to operate.
The VAZ 2114 is equipped with a three-phase rectifier, which has the following advantages:
- Converts alternating current into direct current with the lowest pulsation frequency: the lower the frequency, the more stable the vehicle’s electronic systems will function;
- Can be equipped with diodes of both bridge and half-bridge types;
- Makes it possible to install a current filter - a capacitor.
Article on the topic: Why the speedometer does not work on the 4: we check the speed sensor The cost of the diode bridge ranges from 500 to 1100 rubles, depending on the manufacturer. The market offers rectifiers both from Chinese companies, which have a low cost and questionable quality, and from well-known brands, the reliability of their products has been tested by many car owners.
As evidenced by reviews from the owners of the fourteenth, devices from LG have proven themselves to be the best. The best option in terms of price-quality ratio is the LG 0108 model. It can also be used as a diode bridge for a VAZ 2115 generator.
Basic faults
Quite often the following picture is observed - the ignition is on, but the generator light on the panel does not light up. This usually indicates that:
- there was a wiring break;
- The fuse has blown.
In this case, check all cables coming from the generator. If damaged wiring is found, it is replaced.
It also happens that:
- the light does not light;
- the battery drains quickly, even if it has just been charged;
- however, the remaining control devices operate normally.
All these signs clearly indicate a malfunction of the generator. Here it is possible that:
- the diode is shorted;
- contact on the winding was lost;
- the traction relay is broken;
- The brush holders have become unusable.
However, quite often all that happens is a wire break between the generator and the dashboard or a light bulb burns out.
If the lamp lights up when the ignition is on and the battery is charged, then you should pay attention to the serviceability of the voltage regulator. When the engine is running, the display lights up too brightly or, conversely, too dimly
Here, perhaps, the problem lies in the low tension of the drive belt. Normally, it should not give in when pressed with a finger more than 10 millimeters. It will also have to be replaced if signs of significant wear are visible on the surface with the naked eye.
When the engine is running, the display lights up too brightly or, conversely, too dimly. Here, perhaps, the problem lies in the low tension of the drive belt. Normally, it should not give in when pressed with a finger more than 10 millimeters. It will also have to be replaced if signs of significant wear are visible on the surface with the naked eye.
Sometimes the generator does not work because the stator winding is shorted to ground or the electrical circuit is broken.
In addition, at the anchor, sometimes the terminals of the contact rings move away from the winding. They can be soldered in place.
Loud noise from the alternator most likely indicates bearing failure.
Generator design on the VAZ-2114
Before you begin directly carrying out repair operations on the generator, you need to know the structure of this spare part.
The generator for VAZ 2113-2115 cars is marked as 37.3701, and it is suitable not only for this family, but also for cars of the GAZ family. So, let's look at what parts this unit is made of.
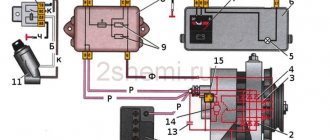
VAZ generator device
Generator 37.3701: 1 – cover on the side of the slip rings; 2 – rectifier block; 3 – rectifier block valve; 4 – screw for fastening the rectifier unit; 5 – contact ring; 6 – rear ball bearing; 7 – capacitor; 8 – rotor shaft; 9 – output “30” of the generator; 10 – output “61” of the generator; 11 – voltage regulator; 12 – terminal “B” of the voltage regulator; 13 – brush; 14 – stud securing the generator to the tension bar; 15 – pulley with fan; 16 – rotor pole piece; 17 – spacer sleeve; 18 – front ball bearing; 19 – drive side cover; 20 – rotor winding; 21 – stator; 22 – stator winding; 23 – rotor pole piece; 24 – buffer sleeve; 25 – bushing; 26 – clamping sleeve