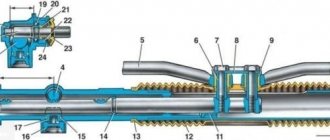
Camshaft VAZ 2107
The camshaft is the main element of the gas distribution mechanism of a car engine. This is an all-metal part, made in the form of a cylinder with support journals and cams placed on it.
The camshaft contains cams and journals
Purpose
The timing shaft is used to control the processes of opening and closing valves in the combustion chambers of the engine. In other words, it synchronizes the operating strokes of the power unit, promptly admitting the fuel-air mixture into the combustion chambers and releasing exhaust gases from them. The camshaft of the “seven” is driven by the rotation of its star (gear), connected through a chain to the crankshaft gear.
Where is it located?
Depending on the design of the engine, the timing shaft may have a different location: upper and lower. With its lower location, it is installed directly in the cylinder block, and with its upper location, it is installed in the cylinder head. For "sevens" the camshaft is located in the upper part of the cylinder head. This arrangement, first of all, makes it easily accessible for repair or replacement, as well as for adjusting valve clearances. In order to get to the timing shaft, just remove the valve cover.
Operating principle
As mentioned, the camshaft is driven by the crankshaft gear. At the same time, its rotation speed, due to the different sizes of the drive gears, is reduced exactly by half. The full operating cycle of the engine occurs in two revolutions of the crankshaft, but the timing shaft makes only one revolution, during which it manages to let the fuel-air mixture into the cylinders one by one and release the exhaust gases.
The opening (closing) of the corresponding valves is ensured by the action of the cams on the valve tappets. It looks something like this. When the shaft rotates, the cam with its protruding side presses the pusher, which transmits force to the spring-loaded valve. The latter opens a window for the intake of the combustible mixture (exhaust of gases). As the cam rotates further, the valve closes under the action of a spring.
The valves open when the protruding parts of the cams press on them
Characteristics of the VAZ 2107 camshaft
The operation of the VAZ 2107 timing shaft is determined by three main parameters:
- phase width - 232o;
- intake valve lag - 40°;
- exhaust valve advance - 42o.
The number of cams on the camshaft corresponds to the number of intake and exhaust valves. The "seven" has eight of them - two for each of the four cylinders.
Find out more about the operation of the timing belt: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/grm/grm-2107/metki-grm-vaz-2107-inzhektor.html
Is it possible to increase the power of a VAZ 2107 engine by installing a different camshaft?
Probably, every owner of the “Seven” wants the engine of his car to work not only without interruptions, but also with maximum efficiency. Therefore, some craftsmen are trying to tune power units using various methods. One of these methods is to install a different, more “advanced” camshaft.
The essence of tuning
Theoretically, it is possible to increase the power performance of a power unit by increasing the phase width and lift height of the intake valve. The first indicator determines the period of time during which the intake valve will be open, and is expressed in the angle of rotation of the timing shaft. For the “seven” it is 232o. The lift height of the intake valve determines the area of the hole through which the fuel-air mixture will be supplied to the combustion chamber. For VAZ 2107 it is 9.5 mm. Thus, again, in theory, as these indicators increase, we get a larger volume of combustible mixture in the cylinders, which can really have a positive effect on the power of the power unit.
The phase width and lift height of the intake valve can be increased by changing the configuration of the corresponding cams of the gas distribution shaft. Since such work cannot be done in a garage, for such tuning it is better to use a finished part from another car.
Camshaft from Niva
There is only one car whose camshaft is suitable for the “seven”. This is a VAZ 21213 Niva. Its timing shaft has a phase width of 283°, and the intake valve lift is 10.7 mm. Will installing such a part on a VAZ 2107 engine give anything in reality? Practice shows that yes, there is a slight improvement in the operation of the power unit. The power increase is approximately 2 liters. s., but only at low revs. Yes, the “seven” responds a little sharper to pressing the accelerator pedal at the start, but once it gains speed, its power becomes the same.
Sports camshafts
In addition to the timing shaft from Niva, the VAZ 2107 can also be equipped with one of the shafts made specifically for “sports” tuning of power units. Such parts are produced by a number of domestic enterprises. Their cost ranges from 4,000–10,000 rubles. Let's look at the characteristics of such camshafts.
Table: main characteristics of “sports” timing shafts for VAZ 2101–2107
| Name | Phase width, 0 | Valve lift height, mm |
| "Estonian" | 256 | 10,5 |
| "Estonian +" | 289 | 11,2 |
| "Estonian-M" | 256 | 11,33 |
| Shrik-1 | 296 | 11,8 |
| "Shrik-3" | 304 | 12,1 |
Malfunctions of the VAZ 2107 camshaft, their symptoms and causes
Considering that the timing shaft is subject to constant dynamic and temperature loads, it cannot last forever. It is difficult even for a specialist to determine that this particular unit has failed without detailed diagnostics and troubleshooting. There may be only two signs of its malfunction: a decrease in power and a quiet knocking sound, which manifests itself mainly under load.
The main camshaft faults include:
- wear of the working bodies of the cams;
- wear of the surfaces of the bearing journals;
- deformation of the entire part;
- shaft fracture.
More about timing chain repair: https://bumper.guru/klassicheskie-modeli-vaz/grm/grm-2107/kak-natyanut-tsep-na-vaz-2107.html
Wear of cams and journals
Wear is a natural occurrence for a constantly rotating part, but in some cases it can be excessive and premature. This leads to:
- insufficient oil pressure in the system, as a result of which lubricant does not flow to loaded areas or is supplied in smaller quantities;
- low-quality motor oil or one that does not meet established requirements;
- defect in the production of the shaft or its “bed”.
If the cams wear out, the engine power is noticeably reduced, since they, being worn out, cannot provide either the appropriate phase width or the required lift of the intake valve.
When the cams wear out, engine power drops
Deformation
Camshaft deformation occurs as a result of severe overheating caused by malfunctions of the lubrication or cooling systems. At the initial stage, this malfunction may manifest itself in the form of a characteristic knocking sound. If you suspect such a breakdown, further operation of the car is not recommended, as it can damage the entire gas distribution mechanism of the engine.
Deformation occurs due to malfunctions in the lubrication and cooling systems
Fracture
A camshaft fracture may be a consequence of its deformation, as well as poor timing. In the event of this malfunction, engine operation stops. In parallel with this problem, others arise: destruction of the shaft “bed”, bending of valves, guides, damage to parts of the piston group.
A shaft fracture may be a consequence of deformation
Block plane and broken gasket
A “punched” cylinder head gasket on Nivas and Shnivas is a birth defect. At some point they just went en masse. There is no need to be surprised. With modifications to the engine to meet new environmental standards, the designers are pushing the fan operating temperature further and further. This gives us an element of “glow” ignition. At a mileage of 15-25 thousand, the cylinder head gasket breaks, and so on down the list. Antifreeze to oil, oil to antifreeze. What do they do in the Papuan service? They buy a Fritex metal bag, install it, and 10 thousand later the client comes back with a new one, with the same question. Or rather, with two. How long? And the classic “what should I do?” It is not the Niva cylinder head gaskets or bolts that are to blame, it is the factory quality of processing of the block plane and the cylinder head plane that is to blame. Below I publish a photo of one of the blocks. I personally changed the gasket on it twice until I found the optimal set, which I now recommend. The metal bag does not help, but rather hinders. It cannot be crimped and does not fill uneven surfaces of the block. You need a shrink gasket that will completely accept the topography of the surface and the bolts that will constantly press it. This is the reason why hardened bolts are not rolled here. For a long time, the plant installed the Yaroslavl metal package “Fritex”, and now they have switched again to shrink gaskets. In a decent production facility, it would be easier to update the machine park and equipment, but at AvtoTAZ it turned out to be easier to go back ten steps along the road of technical progress.
Troubleshooting the VAZ 2107 timing shaft
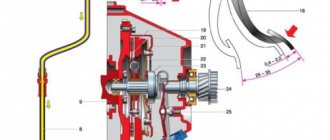
When the camshaft is removed from the “bed”, it is necessary to assess its condition. First this is done visually. The camshaft must be replaced if its working surfaces (cams and bearing journals) have:
- scratches;
- bullies;
- cut wear (for cams);
- enveloping a layer of aluminum from the “bed” (for support necks).
In addition, the camshaft must be replaced if even the slightest traces of deformation are found.
The degree of wear of the support journals and the supports themselves is determined using a micrometer and caliper. The table below shows the permissible diameters of the journals and working surfaces of the supports.
Defect detection is carried out using a micrometer and calipers
Table: permissible diameters of the camshaft journals and its “bed” supports for VZ 2107
| Serial number of the neck (support), starting from the front | Allowable dimensions, mm | |
| Minimum | Maximum | |
| Support journals | ||
| 1 | 45,91 | 45,93 |
| 2 | 45,61 | 45,63 |
| 3 | 45,31 | 45,33 |
| 4 | 45,01 | 45,03 |
| 5 | 43,41 | 43,43 |
| Supports | ||
| 1 | 46,00 | 46,02 |
| 2 | 45,70 | 45,72 |
| 3 | 45,40 | 45,42 |
| 4 | 45,10 | 45,12 |
| 5 | 43,50 | 43,52 |
If during the inspection it is determined that the dimensions of the working surfaces of the parts do not correspond to those given, the camshaft or “bed” must be replaced.
How to choose quality spare parts
Buy a camshaft from a reliable and time-tested company such as PJSC AvtoVAZ. There is a hologram print on the packaging. It flickers in the light and depicts the company logo. There is also a barcode sticker on the box. The product is packaged in blue translucent film. There is a seal from the quality control department inside the package. Buy rockers with adjusting bolts. There are levers of the new and old model. The holes in them vary in diameter and number of cuts. If you buy the arms and bolts separately, they most likely won't fit together.
READ How much oil is in a Hyundai Getz engine
Installing a new camshaft
In order to install a new timing shaft, you will need the same tools as to dismantle it. The installation procedure is as follows:
- Be sure to lubricate the surfaces of the cams, bearing journals and bearings with engine oil.
- We install the camshaft in the “bed”.
- Using a 10 mm wrench, tighten the bolts of the thrust flange.
- We check how the shaft rotates. It should turn easily around its axis.
- We set the shaft to such a position that its pin would coincide with the hole on the fixing flange.
- We install the bed on the studs, screw on the nuts, and tighten them. It is important to follow the established procedure. The tightening torque is in the range of 18.3–22.6 Nm.
The nuts are tightened using a torque wrench with a torque of 18.3–22.6 Nm - We do not install the valve cover and camshaft sprocket in place, since it will still be necessary to set the valve timing.
What is cylinder head bolt pulling used for?
If all the cylinder block bolts are in order and do not require replacement, but the torque is much lower than the values set by the manufacturer, it is necessary to tighten the bolts. To do this you will need the following tool:
- Special torque wrench with torque indicator;
- Calipers or any small ruler.
Pulling the cylinder block bolts takes place in 4 main stages:
- First, using a torque wrench, you need to tighten the bolts in the order indicated in the figure below to a force value of 2.0 kg/cm.
- Then, in the same order, you need to go around the second circle and increase the torque value to 8 kgf/m.
- Upon completion of the work, you will need to tighten the bolts to 90 degrees in the 3rd circle.
Replacing cylinder head bolts and tightening them is a simple process that only requires the use of special tools and skill. If you are performing this type of work for the first time, be sure to monitor the accuracy of the torque and set the correct tightening angle.
Setting ignition timing (valve timing) by marks
After the repair work has been carried out, it is necessary to set the correct ignition timing. To do this you need to do the following:
- Install the camshaft sprocket with the chain, secure it with a bolt without tightening it.
- Install the chain tensioner.
- Place the chain over the crankshaft, accessory shaft and camshaft gears.
- Using a 36mm wrench placed on the crankshaft pulley nut, rotate the crankshaft until the mark on the pulley aligns with the mark on the engine cover.
Labels must match - Determine the position of the camshaft sprocket in relation to the “bed”. The mark on the star should also line up with the protrusion.
If the marks do not match, you need to shift the sprocket relative to the chain - If the marks do not match, unscrew the camshaft sprocket bolt and remove it together with the chain.
- Remove the chain and turn the sprocket to the left or right (depending on where the mark is shifted) by one tooth. Place the chain on the sprocket and install it on the camshaft, securing it with a bolt.
- Check the position of the marks.
- If necessary, repeat shifting the star by one tooth until the marks coincide.
- Upon completion of work, secure the star with a bolt and the bolt with a washer.
- Install the valve cover.
Secure it with nuts. Tighten the nuts in the order shown in the photo. Tightening torque: 5.1–8.2 Nm. The nuts must be tightened with a torque wrench to a torque of 5.1–8.2 Nm - Carry out further engine assembly.
Transfer case
- Nut securing the suspension bracket to the pillow axis M10×1.25 26.5-32.3 (2.7-3.3)
- Nut securing the suspension bracket to the body M8 15.0-18.6(1.53-1.90)
- Nut securing transfer case housing covers, front axle drive housing, speedometer drive housing, control lever bracket M8 14.7-24.5(1.5-2.5)
- Differential lock switch M16×1.5 28.4-45.0 (2.9-4.6) Bolt securing the forks to the gear shift rods MB 11.8-18.6 (1.2-1.9)
- Bolt securing the forks to the differential lock rod M12×1.25 11.7-18.6(1.2-1.9)
- Nut securing the propeller shaft flange to the drive shaft and to the drive shafts of the front and rear axles M16×1.5 96.0-117.6(9.8-12.0)
- Driven gear mounting bolt М10×1.25 66.6-82.3 (6.8-8.4)
- Nut for securing the rear bearing of the drive shaft and the rear bearing of the intermediate shaft M18×1.5 96.0-117.6(9.8-12.0)